What Is the Semantic Web?
The Semantic Web is a network of data that are related in such a way that they can quickly be processed by machines instead of human operators. It can be considered as an extended version of the existing World Wide Web. This version represents an effective means of data representation in the form of a globally linked database. By supporting the addition of semantic content in Web pages, the Semantic Web targets the conversion of the now available web of unstructured documents to a Web of information.
Tim Berners-Lee coined the term Semantic Web during the first World Wide Web conference in 1994. He later emphasized on the concept by publishing two more articles. One in May 2001 and the other in May / June 2006.
Table Of Contents
−- What Is the Semantic Web?
- A Brief Description of The Semantic Web
- Implementing the Semantic Web
- Understanding Semantic Search
- Diving Deeper into Semantic Web and User Intent
- The Purpose of the Semantic Web
- Why Is the Semantic Web More Advantageous?
- Handles That We Need to Overcome
- Advantages of Semantic Web
- Impacts of Semantic Search Engines on SEO
- The Semantic Web and Machine Learning
- How Can Websites Help Search Engines Serve More Relevant Results?
- Is Your Site Ready for Semantic Search?
- How Do You Then Prepare Your Site for Semantic Search?
- Why Should you use LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) Keywords?
- LSI Keywords Versus Long Tail Keywords
- Why Should You Use LSI Keywords in Your Content?
- Using the LSI keywords
- Best Tools to Generate LSI Keywords
- Conclusion

A Brief Description of The Semantic Web
The web is basically arranged as documents which are hyperlinked to each other. Consider this, when you search for particular information, Google’s bots pick up different pieces of information and deliver them to you, the user. Unfortunately, computers and devices do not understand that information.
The semantic web arranges data and information in a structure known as ontologies. This way, related information is stored as a cluster or a taxonomy. Thus, making it easier for computers to deliver more relevant information, as they understand that.
Implementing the Semantic Web
- Ecommerce
There are various ways the semantic web is applied today. We start by demonstrating how the semantic web helps consumers understand the product and purchasing patterns. To do this, we look at a concept developed by Haklae Kim, Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information.
Consider when buying a gaming computer online. Let’s say on Amazon, and you have little information about gaming computers. You don’t have an idea about features and specification to consider but more than willing to make a purchase.
Here is where the semantic web comes in. Using knowledge graphs, it breaks down products features in a way it is easy for every consumer to understand. In other words, it helps structure product data, in this case (features and specifications) in such a way it is machine-readable. This, therefore, make it easier for consumers to query the knowledge graphs to find detailed information about a product hence making a sound decision.
- Within an Organization
Wondering whether you can apply the semantic web to a real situation that is not entirely web-based? An organization is an excellent place to start. For example, you can use the semantic web to solve information management hiccups.
Well, let’s consider a scenario of why information comes to the organization through different channels. For example, through inbound calls, newspaper and emails and stored in various ways such a report, presentation, or stored in an excel sheet.
Now consider when asked to retrieve the information ten years later. It will probably be an uphill task if you don’t remember how that information was stored, or where to start. In other words, it is will tedious and time-consuming trying to recover such information. Worse if the information (email) happened to have been deleted, it even becomes more tedious.
Semantic web comes in to solve issues like information retrieval and storage, first by marking received information with XML. The next step is the digital signing of the XML document. RDF helps in annotation where notes or comments can be added to the XML document. The annotation will also need to be signed, digitally.
The annotations will be necessary for establishing connections and relationships between data. They will help in grouping the data into taxonomies, which will later be integrated into the organization’s database. With the semantic web, retrieval becomes an easy task.
With that in mind, let’s have a look at what an organization needs to use the semantic web.
- Nurture a culture of clear communication within the organization. People in organizations need to understand why information there is a change in information management.
- Define goals that you want to achieve clearly
- Carry out analysis of how different stakeholders would be affected, for example, suppliers
- Put together a team to help communicate the vision
- Get the technical team to start (add XML to documents, build ontologies)
- Help management clearly understand the benefits that come with using the semantic web
- Set a routine staff training schedule and implement
Understanding Semantic Search
Semantic search, even from its name is an aspect of the semantic web that we are already experiencing. It helps in the delivery of more accurate search results by putting into consideration user intent, relationships between words, and meaning in a particular context.
Semantic search was as a result of a Google algorithm update in 2013 known as Hummingbird. Closely related to Hummingbird is RankBrain. Let’s look at these concepts briefly.
- Hummingbird was as a result of the Google algorithm update in 2013, which uses context and user intent to deliver search results. Before Hummingbird, precise keywords were used in ranking. This resulted in some Black Hat SEO tactics like keyword stuffing. Keyword stuffing is the use of the same keyword many times, like 20 times. Today it is recommended to use a single keyword 2- 3 times.
- RankBrain is comparable to Hummingbird, but it is a machine learning system that helps to interpret queries. It also plays a key role by analyzing Google’s index to look for pages with specific features that would be a good fit for the keyed in a query. These features include pages that rank high in search results based on factors like time spent on the page and click-through rate. This update makes sure every use receives a page that matches the motivation behind their search. For example, if a user is asking a question, like “should I update my computer often?” The results page will then feature answers to that question rather than sites to buy organic dog food.
Diving Deeper into Semantic Web and User Intent
User intent
Here is an excellent example to explain user intent. When you are watching your favorite volleyball team, one thing that you probably follow is the live score updates. The live score updates here become user intent. User intent becomes the real thing that the internet user is looking for.
From the example, while the user intent is live score updates, the user may type in “football match today” into a search engine when they want to watch a match. The search engine needs to understand that what the user is actually looking for is live scores and not football match of that day. This is a clear illustration that keywords and user intent are quite different.
Now, how can search engines serve results that meet user intent?
Search engines can do so by studying internet users’ behavior. For example, if you think that a particular website is useful, you will first click on the link and probably skim through the content. If the site contains information that addresses your intent, you will actually spend more time on the site.
Time spent on websites, click-through rates, and bounce rates become the standard by which search engines pick the results to serve. So, when a user types in a keyword, Google shows the pages that are similar to what other users who typed in similar keywords found useful and relevant. Thus, such pages are said to have met the user’s intent.
The Purpose of the Semantic Web
The sole purpose of the semantic web is to give users the best internet experience possible. And it does so by trying to address user intent. This involves explicitly decreasing and eliminating the reliance on document and hyperlinks as the primary means of information retrieval. It further makes it possible to use the relationship between words and concepts in various taxonomies.
Why Is the Semantic Web More Advantageous?
- Relationship between data is based on meaning: Semantics from a language point of view implies meaning. So, the relationship between data is not based on its structure but on meaning.
- Makes it possible for computers to achieve comprehension of data the same way human do: Once data is well interlinked, it will be possible for computers and humans to cooperate. A good example is how Google is now able to use personal data to make suggestions. For example, you may find Google suggesting events near you by simply analyzing your personal data. This is happening because Google has managed to build knowledge graphs based on user behavior and facts.
Another example is Cortana. By asking or correcting information about you, soon you will see receiving more relevant search results. All this is happening because of knowledge graphs modern machines are able to keep and use.
- The ability of organizations to build knowledge graphs: Businesses and organizations today can create knowledge graphs from the data/ information they collect. Such information is a goldmine when it comes to content marketing, improved user experience, and organic marketing. Besides, knowledge graphs can help businesses understand their customers more. For example, what they like doing or why they spend most of the time.
- Google can now serve more accurate search results: Machines are becoming more and more intelligent each day. This is happening because they can find and connect facts which is essential in driving knowledge graphs for search engines.
- In fighting fake news: Semantic web is making it easier to trace the source of fake news.
- Increases security: This technology allows for smart data encryption. Besides, it allows for even more sophisticated data access controls that enable even digital signing of content and emails.
Handles That We Need to Overcome
- Insufficient data: Organizations, as well as users, still have not shared enough information. This, therefore, creates a challenge when it comes to linking data on the web. Only when reliable data is shared, this will be possible.
- Ambiguity: For example, how can you tell a specific name refers to an individual in context A or in context B, or between two different applications? Without a robust, shared knowledge base, it is challenging to parse ambiguity between words and phrases.
Advantages of Semantic Web
- Helps with information retrieval: Semantic web stores data and information in a knowledge graph which are used to understand the context of a query in order to assign specific meaning to user intents. That relationship helps increase the specificity of search queries, as well as the information retrieved to serve more accurate search results. Eventually, this results in fast information retrieval.
- Help answer complex questions: The relationship among ontologies makes it possible to answer complex questions. Ontologies are basic components of the semantic web that help defines relations between terms. For example, they help build a relationship between location and postal codes. Or phone numbers and country of origin.
- Help in automatic summarization: The semantic web plays a significant role in content summarization based on facts extracted. A good example is a digital signature. It helps you verify the information received is coming from a reliable source. For example, a law firm, bank or a recognized institution. Ideally, the semantic web allows agents to exchange ontologies, making it possible to have a common reference point.
- Data sharing: A good example is social media platforms. Semantic web allowing us to interlink data in a machine-readable way make it possible for communication to happen. Otherwise, it will not be possible to communicate online and via social media as we do today.
Impacts of Semantic Search Engines on SEO
Over the years, a lot of SEO techniques have changed drastically. But there is one thing has remained fairly unabated all the same amid a wave of changes. The SEO world is still primarily driven by keyword phrases. Use of keywords in the URL structure, meta-tagging, links, contents, and in everything of the search engine optimization world is seen. So, keywords are ubiquitous in the SEO field, regardless of the ways taken by SEO experts to slice it. With Panda updates, it was apprehended that there might come a new surge which could tweak and throw all questionable SEO practices.
This implies focusing more on creating content that is relevant to the keyword topic, not just the keyword. It also means placing a greater priority on matching content to the user’s search intent. That will mean answering questions thoroughly, providing detailed instructions and creating optimized and targeted landing pages.
Anyway, keywords are still a relatively prime factor in SEO practice. The semantic web search seems to add a whole new element to this world, and that is the human element. With its advent, SEO professionals are required to figure out the actual meaning of the keyword they are using and to create content accordingly and precisely. So, outlook to the keyword application for the SEO purposes needs to be changed to live up to the parameters of the semantic search engines. At the same time, keyword relevancy, not semantics, will always be of first consideration for all search engines. The only approach to it is going to change.
The Semantic Web and Machine Learning
If you are keen today, you may have noticed we are slowly moving from typing keywords on search engines like Yahoo, Google, and Bing to voice search, and conversational search. What you are seeing is aimed at getting to the user intent so that the response served is relevant, accurate and faster. To understand this concept further, let’s have a look at the semantic web that allows you to “talk back” to search engines.
The possibility of computers talking back search engines was first heard in 2013 during a Google I/O developer conference. Since then, the world has seen significant advancements, resulting in conversational search. Here is an example, if you ask Google “how is Messi”, it will be able to give you an answer. Besides, if you still ask follow-up questions like “how many siblings does Messi have” google will also answer. It is that exciting.
Advanced Forms of Semantic Search
- Google Now
We start by having a look at Google Now, which will help you understands how Google Home and Amazon Alexa work. In simple terms, Google Now is an interactive agent, intelligent agent or simply a context engine that can understand user intent and respond with relevant results.
Google Now works by creating a context and responding based on that. Let’s see an example that will help you understand this. If on vacation and ask “what to eat”, Google Now will respond with a few suggestions. A change of location (you been in a different location) is what is triggering Google Now to respond with accurate suggestions. Google will detect the change of location and know that your intent might include finding a new restaurant.
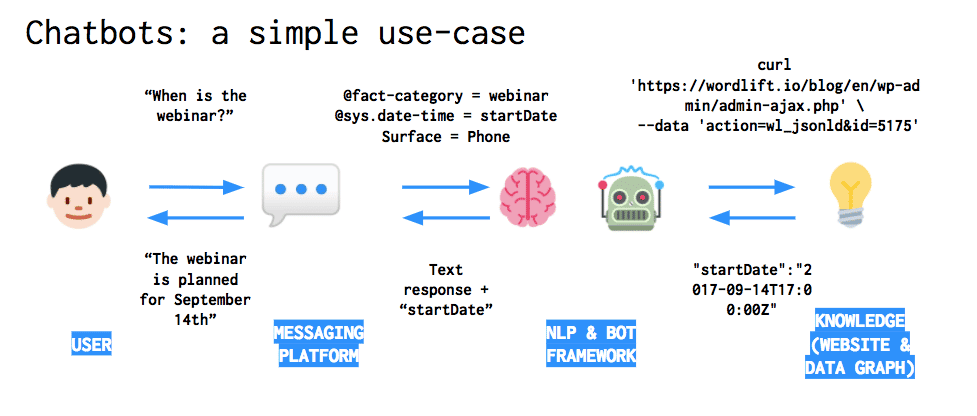
- Chatbots
The growth of artificial intelligence is now in full swing and chatbots are in the front lead of the huge wave of progress. Currently, the number of users of messaging apps like Skype, Slack, WhatsApp, and their analogs is skyrocketing. It is good to note opportunities provided by chatbot systems go far beyond giving responses to customers’ inquiries. For example, they play a crucial role in collecting information, reducing overhead cost and helping organize meetings within organizations.
Types of chatbots
- Simple chatbots: Working according to pre-prepared commands. Respond to specific commands.
- Smart chatbots: Powered by machine learning/artificial intelligence. Also known as an advanced chatbot.
How Can Websites Help Search Engines Serve More Relevant Results?
We have talked about interactive agent like Google Now without a mention of websites. Now to help you understand this, ask yourself this question, why do interactive agents like Google Now get the relevant results it suggests? The answer is very simple, from websites. In other words, this means sites are not left behind and have to do more to facilitate information retrieval. But how is this possible? Let’s have a look at these two concepts.
- Original, high-quality, and relevant content
This emphasizes on webmasters understanding their target audience and their needs before creating any content. For example, using artificial intelligence tools to link data and entities on your WordPress site will help build your own knowledge graph for your website, relevant to your site’s topic. Consequently, interactive agents will be able to query those knowledge graphs and return more accurate results.
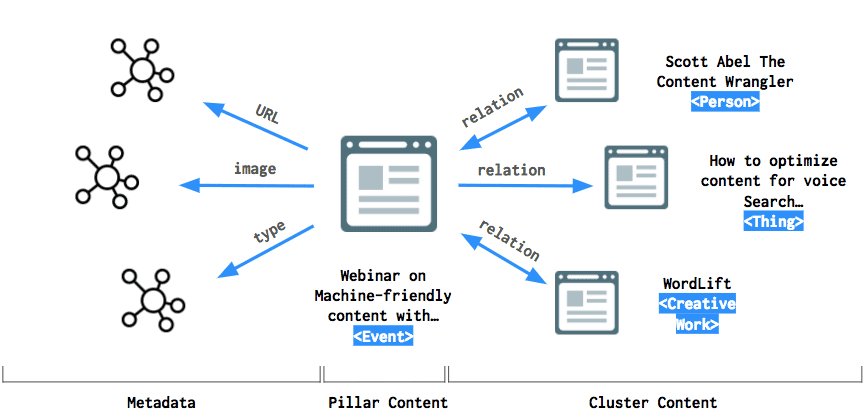
- Schema.org
This refers to the management of structured data on the internet, on web pages, in emails messages and beyond that helps search engines parse the meaning from human language. This happens because of the connections formed by the linked data in the markup.
Is Your Site Ready for Semantic Search?
The future of the semantic web is already with us here though not completely, but at least we can feel the impact. Now let’s have a look at few concepts.
- Linked Data
This refers to a way of structuring information in ways computers can understand. A good example is how Google used knowledge graphs to enhance search results with regards to user intent.
- Voice Search
Software agents like Google Now and Apple’s Siri are a good example of software agents (able to work across different platforms) using voice search to help do a lot. For example, they can make recommendations for hotel rooms and predict user needs.
- Featured Snippets
When you search for something using any search engine, sometimes you notice a result above the rest in a block, with a summary of the answer and a link to the website it is derived from. This is a featured snippet. Note that these featured websites are chosen by Google, based on how well they address user intent. If your site is featured, you will get higher traffic, which could translate to conversions, based on what your site is all about.
How Do You Then Prepare Your Site for Semantic Search?
Here is how you can prepare your site for the aspects of it that have already rolled out.
- Create customer personas: To serve your customers better, it is essential you understand user intent. You can do this by looking for information that your site has or could provide. Once you do (understand user intent), building customer personas will be easy. A/B testing and analytics will also help in recognizing your real customers based on demographics like age, gender, and location.
- Long-tail keywords: Long-tail keywords are those that contain three or more words and play a key role in making sure relevant search are served. Often, users using these keywords are looking for specific information. Thus, ranking for long-tail keywords get you closer to user intent.
Why Should you use LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) Keywords?
LSI Keywords are conceptually related terms used by search engines use to understand the content on a webpage deeply. Let’s dive deeper and understand this concept.
For example, let’s say you just published content about cold brew coffee. Google will scan your page to see whether you use the term “cold brew coffee” in your image alt text, title tag, or content. Further, they will also scan your page for LSI keywords like “cold water”, “filter”, “grind”, “ice” and “temperature”. And when they locate LSI keywords in your content, they will conclude your page is about the topic of cold brew coffee.
LSI Keywords Versus Long Tail Keywords
As we said earlier, long-tail keywords contain at least three words. They are characterized by length and not necessarily related to the main keyword. For example, when searching for digital services, you may want to make your search more specific. For example, “Digital services in Miami, FL.”
On the other hand, LSI keywords would have been keywords like “online services in Miami, FL”. Online and digital are not synonym but are related. Hence LSI keywords are used to broaden your search.
Why Should You Use LSI Keywords in Your Content?
- Helps your content not to be flagged as spam: Instead of using the same keywords over and over again, resulting in keyword stuffing. LSI keywords help increase content’s credibility, differentiating it from spun content.
- Gives you unique content ideas: Searching Google for LSI keywords shows you related keywords you can use to create new content. So, if looking to create unique content, remember to factor them.
- Delivers relevant results: LSI keywords play a significant role in SEO. By allowing you to cover more combination of the target keywords, your content rank higher on search results. For example, you will find LSI keywords very helpful in your PPC campaign. This is because by using them, your PPC campaign is likely to perform better as they reach more people.
- Helps in image optimization: When you need to use an image more than once, LSI keywords come in handy. You will use different captions to name your image. This helps in image optimization.
Using the LSI keywords
How should you use these LSI keywords?
- Placement: Don’t force them in your content. Include them naturally; otherwise, they will not enhance the value of your content.
- Relevancy: Make sure to use only those LSI keywords that are relevant to your content. Trying to use the irrelevant LSI keywords could make look like you are trying to appear relevant to two unrelated topics.
- Duplication: Make sure to eliminate duplicate LSI keywords. It is possible to have them, especially when using more than one LSI keyword generation tool.
Best Tools to Generate LSI Keywords
Here is a list of both free and paid tools. Feel free to find more information about each tool.
Conclusion
The semantic web will create a better world where information is served directly to the user, in the shortest time possible. Since information will be stored in ontologies, it is very easy to retrieve it since the relationship between entities will be clearly defined and easy to trace. It is upon us now to start making use of the data we can access and store it in a structured way. And when 3.0 finally kicks in, we will be far miles ahead.
References
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1570826817300343
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1570826817300148
Daconta, C. M., Obrst, J. O. & Smith, T. K. (2003). The Semantic Web: A Guide to the Future of XML, Web Services, and Knowledge Management, 1190-1204.
https://www.cambridgesemantics.com/semantic-university/introduction-semantic-web
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/20140324055730-14091619-effects-of-web-3-0-in-the-new-digital-world
https://chatbotsmagazine.com/the-complete-beginner-s-guide-to-chatbots-8280b7b906ca
http://mashable.com/2013/05/22/chrome-conversational-search/#E_zOAAx3caqB
https://www.lifewire.com/google-now-1616711
https://www.recode.net/2014/8/4/11629480/ten-things-you-didnt-know-that-google-now-could-do

Jay
I've worked for WooRank, SEOptimer, and working on a cool SEO audit tool called SiteGuru.co. Now I have build Linkilo and SEO RANK SERP WordPress theme. I've been in the SEO industry for more than 5 years, learning from the ground up. I've worked on many startups, but also have my own affiliate sites.
TRY OUR FULLY SEO-OPTIMIZED WORDPRESS THEME FOR AFFILIATE MARKETERS!
No need to hire SEO experts anymore to fix your site technical SEO issues
IMPROVE YOUR SITES RANKING TODAY